



Next: 2. Introduction
Up: 1. Preface
Previous: 1. Preface
Contents
Index
GMT 4 represents a major overhaul of the package, hence the major version number increment. There are four
categories of changes that have been implemented:
- Time-series support.
- GMT can now read and write time-series data where
the time coordinates are of the form dateTclock1.2. The formats
used for date and clock are under the user's control. Both Gregorian
and ISO calendars are supported. Frame annotation for time-series are now supported
via the -B option; there are many new modifiers reflecting the vast number of
ways one may want to annotate time axes, including support for primary and secondary
annotation levels and the day- and month-names in numerous languages (send us the information
we need if your language is not supported). The capability to handle time (in -R,
-J, -B, i/o, and plotting) required considerable changes ``under the hood'',
including the introduction of numerous new gmtdefaults parameters to make
the time series support as ``generic'' as we need it to be.
- New Tools.
- Three new tools have been added:
- gmt2rgb: Makes red, green, and blue component gridfiles from an image (to be
used with new options for false color imaging or image draping by grdimage or grdview).
- grdblend: Blends several partially over-lapping grdfiles into one combined grid. Output
grid is written one row at the time so truly enormous grids can be created.
- pslegend: Designs and plots elaborate legends on maps.
- New Program Options.
- Many programs have received additional options or
features that enhances their usefulness:
- blockmean: New option -Sw will return weight sum while -Sz returns
the data sums (i.e., it duplicates the previous -S option).
- filter1d: New filters -Fl
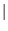 L
L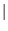 u
u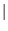 U that return extreme (min, max) values.
U that return extreme (min, max) values.
- gmtconvert: Added new options -F, -A, and -I that simulate
UNIX cut, paste, and tail -r (or tac) capabilities.
Option -E reports first and last point per segment only, -L lists the segment headers only,
while -S lists records from segments whose header matches a given text pattern.
- gmtmath: Added new operators for solving least squares problems (COL, LSQFIT),
finding function roots (ROOTS), and evaluating critical values (CHICRIT, FCRIT, TCRIT, ZCRIT).
We also added some general functions (SINC, LOG2, LRAND) and miscellaneous operations (FLIPUD, NEQ).
The -S option may now take a modifier to select first or last record only.
- gmtselect: New option -Z to pass or skip based on input
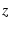 -range.
-range.
- grd2cpt: New options -Q for logarithmic scales, -E for equidistant color
intervals, -R for selecting a grid sub-region, and -N to suppress output of B, F, N colors1.3.
- grd2xyz: New option -W to write a constant weight factor as a 4th output column,
and ability to process several grid files at the same time.
- grdcontour: Expanded the -G option to handle 5 algorithms (4 new) for the placement
of contour labels.
- grdedit: New option -N to replace selected node values given x, y, z data
in table form (options -H, -b, -f, and -: added for file support).
- grdfilter: New geospatial filters -Fl
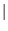 L
L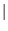 u
u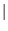 U that return extreme (min, max) values.
U that return extreme (min, max) values.
- grdimage: New option for colormasking (-Q; PostScript Level 3 only), PostScript image
interpolation (-E-dpi), and false RGB color image (when given three grids), as well as a modifier to -T
to draw tile outlines.
- grdinfo: New option to create argument for makecpt (-T) and to round-off
region boundary coordinates (-I).
- grdmath: Added new operators for critical values (CHICRIT, FCRIT, TCRIT, ZCRIT),
geospatial analysis (LDIST, PDIST, INSIDE) and for calculating azimuths (CAS, SAZ). We have
also added some general functions (SINC, LOG2, LRAND) and a few grid operations (FLIPLR, FLIPUD, ROTX, ROTY, NEQ,
INRANGE). We may now create multiple output grids from a single command.
- grdproject: Option to supply false easting/northing or other offsets from the origin(-C).
- grdreformat: Option to suppress header in raw output (-N).
- grdsample: Option to push the bilinear interpolation closer to nodes that are NaN (-Q).
- grdtrack: Options to retrieve nearest node value (-N, no interpolation) and to push
the bilinear interpolation closer to nodes that are NaN (-Q).
- grdview: Colormasking (-Qc, PS Level 3 only), draping of images via red, green,
and blue component grids (-G). Also, drapegrids can have higher resolution than the relief grid, and we
added a modifier to -T to draw tile outlines.
- makecpt: New options -Q for logarithmic scales and -N to suppress output
of B, F, N colors.
- mapproject: New options for datum conversions (-T, -E, and -Q), azimuth and
back-azimuth (-A), distance to point (-G) and line (-L)calculations, and optional false easting/northing (-C).
- minmax: Added -Tdz option to produce -T string for makecpt,
-E for returning extreme records, and the -I option was extended to handle any number of columns when -C is used.
- psbasemap: Extended -L to allow alternate label and justification, and added -T
for directional rose ornament or magnetic compass directions.
- pscoast: Extended -L to allow alternate label and justification, and added -T
for directional rose ornament or magnetic compass directions.
- pscontour: Expanded the -G option to handle 5 algorithms (4 new) for the placement
of contour labels.
- psimage: PostScript image interpolation (-W-xlength), and justification option
in -C.
- psscale: Options to annotate on opposite side (-A) and to plot back or foreground
triangle only (-E[b
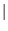 f] ). Also, draw discrete color-key table with centered annotations by appending an optional
gap to the -L option.
f] ). Also, draw discrete color-key table with centered annotations by appending an optional
gap to the -L option.
- pstext: New option -A should azimuths rather than angles be given,
- psxy: Line color control (via -C), symbol position offset (with -D), custom symbols access
(with -Sk; use any of the 35 (Appendix N) that come with GMT or design your own), many new symbols (horizontal and vertical dashes,
pentagon, octagon, rectangle, double-headed and centered vectors), and annotated (``quoted'') lines with -Sq.
- psxyz: Same, plus a vertical dash symbol.
- xyz2grd: Added -Au
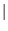 l for upper/lower value at each node.
l for upper/lower value at each node.
- General enhancements.
- These affect most of the programs:
- The coastline data have been updated to GSHHS version 1.3. About 50 or so polygons had lingering
crossovers and some had duplicate points or failed to close; these have now been fixed. Major
errors in the Puget Sound coastline have also been corrected.
- New shorthand to repeat the most recently used projection (-J).
- Options for phase-shifting the stride and supplying a prefix for frame annotations (-B).
- Override GMT defaults directly on the command line with any number of --PAR=value options.
- Now choose from 63 ellipsoids and 223 datums, or use your own values.
- Numerous new GMT defaults parameters, mostly in support of time-series functionality.
- Shorthand for global regions (-Rg for -R0/360/-90/90 and -Rd for -R-180/180/-90/90).
- Full support for either RGB, HSV, or CMYK in pen/fill command-line options or in cpt files.
- Support for English color names (e.g., red, lightbrown).
- Choice of unit when specifying pen thickness (cm, inch, point).
- Easier pen specification mechanism, with predefined names for certain pen thicknesses.
- Centering of plots on current page with -Xc, -Yc.
- More control over input/output table formats (-f, -:[i
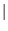 o]).
o]).
- Ability to read and write NOAA/NGDC GRD98 grid format.
- Ability to add additional fonts.
- Custom paper media size (useful for posters and large maps).
- All text are now justified by the PostScript interpreter, as is the clipping of contours and ``quoted lines''
to make space for annotation labels.
- Better support for various international character encodings.
- New Appendices M (color tables), N (custom symbols), O (contours and ``quoted lines''), and P
(using both GMT 3 and 4).
- New hidden files .gmtdefaults4 and .gmtcommands4 to ensure peaceful coexistence with GMT 3-series.
- Data files in directories pointed to by the three environmental parameters $GMT_DATADIR, $GMT_GRIDDIR,
and $GMT_IMGDIR can be specified without their full path names when used as input files.
- We have added five new examples for a total of 25.
- Bourne shell utility gmtswitch simplifies switching between installed GMT versions.




Next: 2. Introduction
Up: 1. Preface
Previous: 1. Preface
Contents
Index
Paul Wessel
2004-10-01
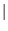 L
L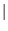 u
u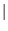 U that return extreme (min, max) values.
U that return extreme (min, max) values.
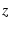 -range.
-range.
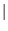 L
L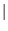 u
u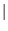 U that return extreme (min, max) values.
U that return extreme (min, max) values.
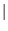 f] ). Also, draw discrete color-key table with centered annotations by appending an optional
gap to the -L option.
f] ). Also, draw discrete color-key table with centered annotations by appending an optional
gap to the -L option.
 l for upper/lower value at each node.
l for upper/lower value at each node.
 o]).
o]).